Medical equipment parameters are critical to ensuring optimal and safe performance. In this article, we will explore the importance of these parameters and how they are evaluated in the field of clinical engineering.
Índice del Articulo
Meaning of parameters in medical equipment:
Medical equipment often has a variety of parameters that provide key information about the patient’s condition or the function of the equipment. Here are some examples of common parameters on medical equipment and their meanings:
Blood Pressure:
Blood pressure is made up of two key parameters: systolic pressure, which is the blood pressure when the heart beats, and diastolic pressure, which is the blood pressure between heartbeats. These values are critical to assessing cardiovascular health, as they indicate the strength of blood flow in the arteries. Understanding both parameters is essential in the comprehensive assessment of blood pressure and its implications for health.
Heart Rate:
Heart rate is defined as the number of heartbeats per minute. This parameter is essential for measuring the electrical activity of the heart and is crucial in assessing cardiac function. Heart rate provides key information about the rhythm and overall health of the heart, being a fundamental indicator for monitoring and assessing cardiovascular activity.
Oxygen Saturation (SpO2):
Oxygen saturation (SpO2) is defined as the percentage of oxygen saturation in hemoglobin. This parameter is crucial as it indicates the efficiency with which the lungs transfer oxygen to the blood. SpO2 is a fundamental indicator in monitoring respiration, providing essential information about body oxygenation and respiratory health.
Respiratory Rate:
Respiratory rate refers to the number of breaths per minute. This parameter is essential for assessing respiratory function and plays a crucial role in monitoring lung ventilation. Respiratory rate provides key information about the health and efficiency of the respiratory system, being an important indicator in the clinical assessment of lung function.
Body Temperature:
Body temperature is defined as the measure of body temperature. This parameter is crucial as it indicates the presence of fever or hypothermia, being a potential indicator of infections or other medical conditions. Accurate measurement of body temperature is essential for clinical assessment and diagnosis, allowing the identification of potential health problems.
Blood Gas Levels (pH, pCO2, pO2):
Blood gas levels, which include pH (a measure of the acidity or alkalinity of the blood), pCO2 (partial pressure of carbon dioxide in the blood), and pO2 (partial pressure of oxygen in the blood), are crucial parameters for assessing respiratory function and acid-base balance in the body. These indicators provide essential information about the efficiency of breathing and oxygenation of the blood, and are fundamental in the clinical assessment of respiratory and metabolic health.
Other Hemodynamic Measures:
Hemodynamic measures, which include parameters such as cardiac output, central venous pressure (CVP), and vascular resistance, are crucial indicators of cardiac and circulatory function. These parameters provide valuable information about the performance of the heart and blood circulation, and are fundamental in the clinical assessment of the patient’s cardiovascular and circulatory health.
Neuromonitoring Parameters:
Neuromonitoring parameters, such as brain electrical activity (EEG) and intracranial pressure (ICP), are key indicators of brain function and pressure within the skull. These parameters allow for the assessment of brain activity and monitoring of pressure in the brain, and are especially useful in cases of head trauma or neurological conditions. They provide critical information for the diagnosis and treatment of patients with neurological impairments.
Medical Imaging Parameters:
Medical imaging parameters, which encompass technical aspects of CT, MRI, and ultrasound, include details such as resolution and contrast. The quality and information provided by these medical images are determined by these technical parameters. These aspects are critical to ensuring high-quality images that facilitate accurate diagnosis and contribute to clinical decision-making.
Anesthesia Equipment Parameters:
Anesthesia equipment parameters, such as respiratory parameters and anesthetic gas concentration, provide relevant information during surgical procedures. These parameters are crucial for monitoring ventilation, oxygenation and gas concentration during anesthesia administration, ensuring safe and controlled conditions during surgery.
It is important to understand and interpret these parameters properly to ensure safe and effective medical care. Furthermore, the interpretation of the parameters may vary depending on the clinical context and the specific condition of the patient.
Importance of parameter evaluation in medical equipment:
The evaluation of parameters in medical equipment is of vital importance in healthcare for several fundamental reasons. These parameters provide valuable information about the patient’s condition and the functionality of the equipment, allowing healthcare professionals to make informed decisions and deliver high-quality care. Here are some key reasons for the importance of parameter evaluation in medical equipment:
Continuous Monitoring:
Constant evaluation of parameters such as blood pressure, heart rate, and oxygen saturation allows for continuous monitoring of the patient’s condition. This is essential for early detection of changes in clinical condition and rapid response to emergency situations.
Accurate Diagnosis:
Parameters provide objective information that contributes to the accurate diagnosis of diseases and medical conditions. Accurate measurement of parameters such as temperature, blood gas levels, and brain activity helps healthcare professionals to properly identify and treat conditions.
Chronic Disease Management:
For chronic diseases, regular assessment of parameters such as blood glucose, blood pressure, and other indicators is critical to effective disease management. It allows for proactive adjustment of treatments and care strategies.
Patient Safety:
Parameter assessment is essential to ensure patient safety during medical procedures and treatment delivery. Medical equipment that accurately monitors parameters contributes to the prevention of medical errors and patient safety.
Treatment Optimization:
Parameter assessment helps healthcare professionals optimize treatments based on individual patient response. It allows for adjustment of drug doses, ventilation modes, and other aspects of treatment to maximize efficacy and minimize side effects.
Preventing Complications:
Monitoring specific parameters, such as intracranial pressure in neurocritical patients or ventilator pressure during mechanical ventilation, helps prevent complications and optimize care in critical situations.
Personalization of Care:
Parameter assessment allows for the personalization of medical care to the individual needs of each patient. This is particularly important in the context of precision medicine and patient-centered care.
Identifying Equipment Failures:
Constant assessment of parameters in medical equipment helps to identify potential failures or malfunctions. This is crucial to ensure the reliability and safety of devices used in healthcare.
Making Immediate Decisions:
Real-time parameters allow healthcare professionals to make immediate decisions about patient management. This is critical in settings such as the intensive care unit (ICU) and emergency situations.
Compliance with Regulations and Standards:
Assessing parameters in medical equipment contributes to compliance with regulations and quality standards in healthcare. Ensures that devices meet regulatory requirements and provide reliable results.
In short, parameter assessment in medical equipment is essential to deliver safe, accurate and personalized healthcare. It contributes to informed decision making, continuous patient monitoring and prevention of complications, thus improving the overall quality of healthcare.
Procedures for evaluating parameters in medical equipment:
The evaluation of parameters in medical equipment involves a series of specific procedures that ensure the accuracy and reliability of measurements. These procedures may vary depending on the type of equipment and the parameters being evaluated, but in general, some standard practices are followed. Here are some common procedures for the evaluation of parameters in medical equipment:
Calibration:
Calibration is an essential procedure that involves regularly performing adjustments to the sensors and components of medical equipment, using reference patterns and standards to ensure accurate measurements. The importance of calibration lies in ensuring that the equipment provides accurate and reliable measurements, contributing to the accuracy and reliability of the results obtained.
Functionality Verification:
Functionality verification involves performing tests according to the manufacturer’s specifications to confirm that the equipment responds appropriately to stimuli or changes in parameters. The importance of this procedure lies in ensuring that the equipment is in a condition to operate correctly, ensuring its functionality and proper performance.
Quality Control (QC):
Quality control (QC) involves implementing periodic programs that include performing specific tests using solutions or simulators. This procedure is crucial as it monitors the stability and accuracy of the equipment over time, ensuring that a consistent level of quality is maintained in the measurements and operations of the medical equipment.
Preventive Maintenance:
Preventive maintenance involves following a program as recommended by the manufacturer, performing regular inspections, cleaning and adjustments. The importance lies in preventing failures and ensuring the long-term performance of the medical equipment, contributing to its reliability and prolonging its useful life.
Verification of Measurement Accuracy:
Verification of measurement accuracy involves comparing the results of the equipment with known standards and ensuring that they are within established accuracy limits. This practice is crucial to assess the accuracy and reliability of the measurements made by the equipment.
Functional Testing:
Functional testing involves performing specific tests for each measured parameter, verifying the response of the equipment to different conditions and measurement ranges. This practice is crucial to assessing the equipment’s ability to operate effectively in various situations.
Tracking Manufacturer Updates:
Tracking manufacturer updates involves staying informed about updates and revisions provided by the manufacturer, and implementing them to the equipment, either in terms of software or firmware, as needed. This practice ensures that the equipment is up to date with improvements and fixes provided by the manufacturer.
Staff Training:
Staff training involves providing regular training to those who operate the equipment, ensuring they are familiar with assessment and maintenance procedures. This practice is crucial to minimizing operational errors and ensuring proper use of the equipment.
Data Logging and Auditing:
Data logging and auditing involves keeping detailed records of assessments and interventions, as well as conducting internal audits to review procedures and results. This practice is critical to providing documentation that supports traceability and facilitates continuous improvement.
Regulatory Compliance:
Regulatory compliance involves ensuring that the equipment meets applicable regulatory requirements and standards. Audits are carried out to verify compliance with local and international regulations, which is crucial to ensure the safety and legality of the use of medical equipment.
These procedures are part of a comprehensive approach to ensure the accuracy and reliability of medical equipment, thus contributing to patient safety and the quality of medical care. It is crucial to follow the manufacturer’s recommendations and develop specific protocols for each type of equipment and parameter evaluated.
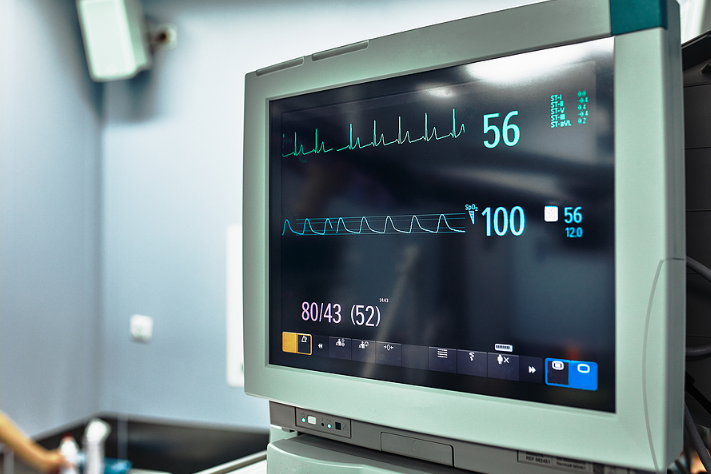
Recording and monitoring parameters in medical equipment:
Recording and tracking parameters on medical equipment are fundamental practices to ensure quality and safety in healthcare. Here are key steps to establishing an effective system for recording and tracking parameters on medical equipment:
Identifying Relevant Parameters:
Identify the critical parameters that must be recorded and tracked for each type of medical equipment. These may include vital data, blood gas levels, electrical signals, among others.
Establishing Recording Protocols:
Develop standardized protocols for recording each parameter. These protocols should include details on the recording frequency, recording format, and specific procedures for each parameter.
Using Recording Software:
Implement electronic recording systems or specific software for data capture and storage. These systems facilitate data entry, reduce manual errors, and allow faster access to information.
Manual Recording:
In situations where an electronic system is not used, establish clear procedures for manual data recording. Ensure staff are trained to keep accurate and legible records.
Assignment of Responsibilities:
Clearly define staff responsibilities in relation to parameter recording. This includes designating who is responsible for making the records, when they should be made and how they should be reviewed.
Recording Frequency:
Determine how often parameters should be recorded. In some cases, continuous recording may be necessary, while in others, periodic recording may be sufficient.
Data Validation:
Implement procedures for data validation. This may include comparing medical equipment readings to known standards or checking the consistency of data over time.
Secure Data Storage:
Ensure secure storage of recorded data. This may include electronic security measures for computer systems or secure physical storage of paper records.
Regular Audits:
Conduct regular audits to review the quality of records and ensure that established protocols are being followed. Audits can also identify areas for improvement and provide feedback.
Implementation of Alerts and Notifications:
Incorporate alerts and notifications into the recording system to highlight abnormal readings or critical situations. This allows for a rapid response to adverse events or significant changes in parameters.
Integration with Electronic Health Records:
Where possible, integrate parameter records with electronic health record systems to facilitate comprehensive access to patient information and promote continuity of care.
Ongoing Staff Training:
Provide ongoing training to staff on recording protocols and the importance of keeping accurate records. This is especially relevant when new equipment or updates to procedures are introduced.
Continuous Review and Improvement:
Establish a continuous process of reviewing and improving recording and tracking procedures. This involves adapting protocols to changing needs and learning from incidents or adverse events.
An effective parameter recording and tracking system on medical equipment contributes to quality care, improves patient safety, and facilitates informed decision-making by medical staff. Consistency in applying these procedures is key to your success.
Frequently Asked Questions about Medical Equipment Parameters:
What are parameters in medical equipment?
Parameters in medical equipment are quantifiable measurements that indicate the status or performance of a device, such as blood pressure on a monitor or heart rate on an electrocardiograph.
Why are parameters important in medical monitoring?
Parameters are crucial for assessing patient health and equipment performance. They provide real-time information that guides clinical decisions and enables rapid intervention in the event of significant changes.
How are parameters calibrated in medical equipment?
Calibration is performed according to specific manufacturer standards and regulations. Regular procedures are carried out to ensure that the equipment provides accurate and consistent measurements.
What are some common examples of parameters in medical equipment?
Examples include heart rate, blood pressure, body temperature, oxygen saturation, and other measures that are critical for monitoring and diagnosis in clinical settings.
What measures are taken to ensure the accuracy of parameters in medical equipment?
Measures include regular calibration, preventative maintenance, verification of accuracy with reference equipment, and ongoing staff training to ensure proper use.
How are alarms related to critical parameters handled?
Medical equipment emits alarms when parameters reach critical levels. Clinical staff are trained to respond to these alarms immediately, taking the necessary measures to ensure patient safety.
What protocols are followed for parameter data management in clinical settings?
Parameter data is managed in accordance with privacy and information security regulations. Records are kept securely and accessible only to authorized personnel.
How does interoperability affect parameter management in medical devices?
Interoperability facilitates the integration of parameter data between different devices and information systems, improving coordination and efficiency in medical care.
Are software updates performed on the equipment to improve parameter measurement?
Yes, software updates are common to improve the accuracy and functionality of medical equipment. These updates should be performed in accordance with the manufacturer’s recommendations and relevant regulations.
How do clinical engineers contribute to parameter management in medical equipment?
Clinical engineers are responsible for monitoring, maintaining and updating medical equipment. They work closely with clinical staff to ensure that parameters are measured accurately and equipment operates safely and efficiently.
Conclusion on Medical Equipment Parameters:
Medical equipment parameters are essential to ensure safe and quality medical care. Regular assessment of these parameters in the field of clinical engineering is crucial to ensure their optimal functioning. Through proper assessment, recording and continuous monitoring, the accuracy and reliability of medical equipment can be improved, thus contributing to the well-being of patients and the success of medical procedures.
Recommendation:
To deepen your knowledge of clinical engineering, I suggest you continue reading the next article that addresses: Clinical Administrative Software.





0 Comments